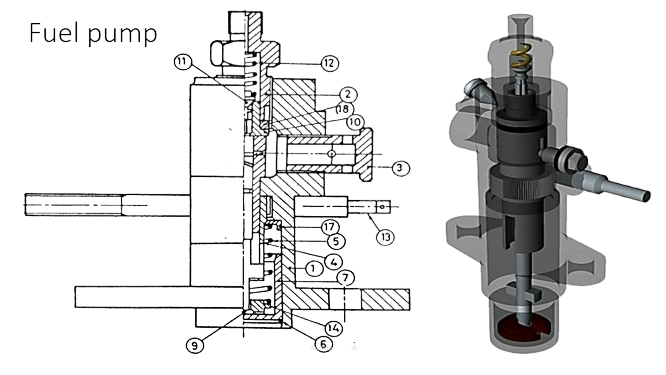
Fuel Injection Pump Components
- Delivery Valve – Ensures the pressurized fuel is sent towards the injector and prevents backflow.
- Inlet Port – Allows fuel to enter the pump from the fuel supply system.
- Spill Port – Provides a path for excess fuel to return to the fuel tank or low-pressure chamber.
- Vertical Hole – A passage inside the plunger allowing fuel flow regulation.
- Helical Groove – Adjusts the fuel quantity delivered to the injector by controlling the fuel spill timing.
- Cylindrical Plunger – Moves up and down to compress and inject fuel under high pressure.
- Barrel – Houses the plunger and provides guidance for its movement.
- Rack – Rotates the plunger to control the fuel injection quantity.
Fuel injection pumps are a crucial component of an internal combustion engine, ensuring the precise delivery of fuel for optimal performance and efficiency. In this guide, we will explore the function, types, and importance of fuel injection pumps in modern vehicles.
What is a Fuel Injection Pump?
A fuel injection pump is a mechanical or electronic device responsible for pressurizing and delivering fuel to the engine’s combustion chamber in precise amounts. It is commonly used in diesel engines and direct fuel injection systems in gasoline engines. The pump ensures proper atomization of fuel, enhancing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions.
Function of a Fuel Injection Pump
The fuel injection pump performs several key functions, including:
- Fuel Pressurization: It increases the fuel pressure to the required level before injecting it into the combustion chamber.
- Accurate Metering: It delivers the right amount of fuel as per engine load and speed.
- Timing Control: It ensures fuel injection occurs at the right moment for efficient combustion.
- Atomization: It sprays fuel in a fine mist for better mixing with air.
- Regulation of Fuel Flow: It adjusts fuel flow based on engine requirements to optimize power and efficiency.
Types of Fuel Injection Pumps
There are several types of fuel injection pumps, each designed for specific applications and engine types. Below are the most common types:
1. Inline Fuel Injection Pump
- Commonly used in heavy-duty diesel engines.
- Has multiple plungers arranged in a line, each serving one cylinder.
- Provides precise fuel delivery and high durability.
2. Distributor (Rotary) Fuel Injection Pump
- Uses a rotating rotor to distribute fuel to multiple cylinders.
- Compact design, making it suitable for smaller diesel engines.
- More efficient and cost-effective compared to inline pumps.
3. Common Rail Fuel Injection Pump
- Used in modern diesel engines.
- Stores fuel in a common rail at high pressure and distributes it to injectors.
- Provides better fuel atomization, reduced emissions, and improved efficiency.
4. Unit Injector System (UIS)
- Integrates the fuel injector and pump into a single unit.
- Each cylinder has its own pump-injector unit.
- Offers high-pressure injection and precise control over fuel delivery.
5. Electronic Fuel Injection Pump
- Found in modern gasoline engines.
- Uses electronic control units (ECUs) to regulate fuel flow.
- Enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
Importance of Fuel Injection Pumps
Fuel injection pumps play a vital role in an engine’s performance by:
- Improving Fuel Efficiency: Ensuring optimal fuel-air mixture for combustion.
- Enhancing Engine Power: Delivering the right amount of fuel for better power output.
- Reducing Emissions: Proper atomization reduces unburned fuel and pollutants.
- Ensuring Engine Longevity: Precise fuel delivery prevents engine wear and tear.
Conclusion
A well-functioning fuel injection pump is essential for the performance, efficiency, and durability of an engine. Understanding its function and types helps in choosing the right pump for specific applications, ensuring optimal engine performance. Whether in diesel or gasoline engines, advancements in fuel injection technology continue to enhance efficiency and environmental compliance in the automotive industry.