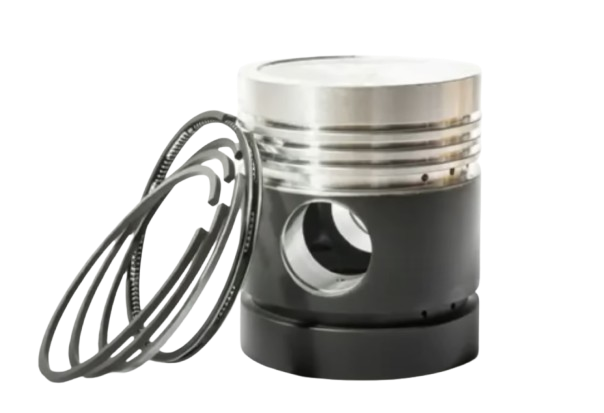
An internal combustion engine’s piston ring is a metallic split ring fastened to the piston’s outer diameter. Usually, they are placed in slots or grooves on the piston itself. These rings operate as a sealing mechanism between the engine’s cylinder’s inner walls and piston.
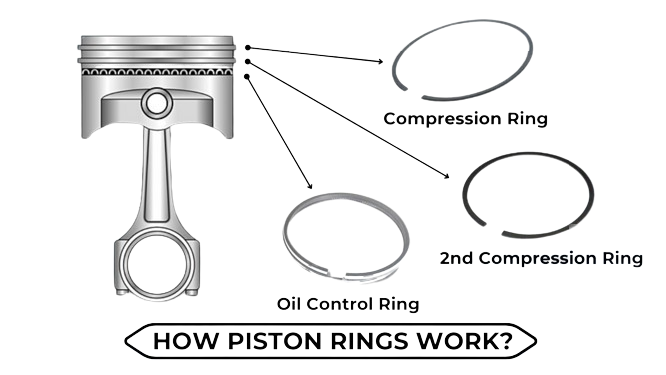
1. Compression Ring
The compression ring is positioned at the top of the piston and is, therefore, responsible for sealing the combustion chamber. Consequently, this seal prevents the high-pressure combustion gases from leaking into the crankcase. Moreover, by ensuring that the gases remain in the combustion chamber, the compression ring allows the engine to maintain the necessary pressure for efficient power generation.
2. 2nd Compression Ring
The second compression ring, also known as the scraper ring, has a dual purpose. It acts as a backup to the first compression ring by further sealing the combustion chamber, preventing blow-by gases from escaping. Additionally, it scrapes any excess oil from the cylinder walls and returns it to the oil pan, ensuring that the engine remains lubricated without excessive oil entering the combustion chamber.
3. Oil Control Ring
The oil control ring, located below the compression rings, plays a vital role in regulating the amount of oil on the cylinder walls. Its main function is to scrape excess oil off the walls and return it to the sump, preventing oil from entering the combustion chamber and causing issues like excessive smoke or fouling of the spark plugs. It ensures that the piston moves smoothly and that the engine remains properly lubricated without wasting oil.
Piston Ring Lifespan: 75,000 to 100,000 Miles


How These Rings Work Together
Each piston ring has a specific role; however, they all work together to maintain engine efficiency and longevity. For instance, the compression rings (top and second) ensure the proper sealing of the combustion chamber, while, on the other hand, the oil control ring regulates lubrication. Consequently, without these rings, the engine would experience a loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and potential damage due to improper lubrication.
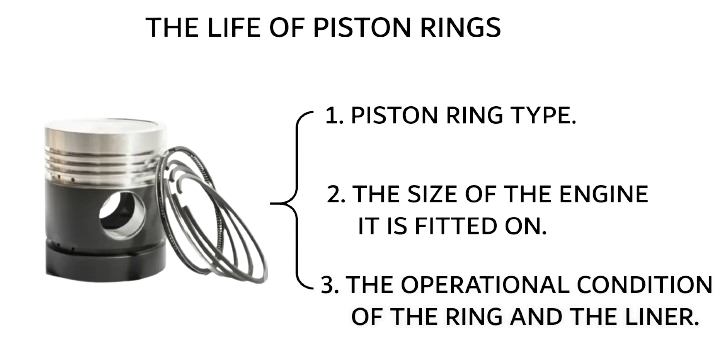

The lifespan of piston rings depends on three main factors:
- Piston Ring Type – Different types of rings are designed for various applications and have varying durability.
- Engine Size – The larger the engine, the more stress is placed on the rings, which can affect their longevity.
- Operational Conditions – How the piston rings and cylinder liner are maintained and used in the engine impacts their wear and lifespan.
These factors together determine how long the piston rings will last before needing replacement.
Conclusion
Understanding how piston rings work is crucial for anyone interested in automotive engineering or engine maintenance. The compression rings ensure that combustion remains effective, while the oil control ring helps maintain optimal lubrication levels. Together, they are key to the engine’s performance, fuel efficiency, and long-term reliability.